1 The dataset
The flights dataset contains daily total delays of major U.S. airlines.
For details, see the corresponding documentation page.
Below, we plot all airports in the dataset.
plotFlights(plotConnections = FALSE, map = "world", xyRatio = 2)
To perform an example application, we follow Section 6 of Hentschel et al. (2022).
The subset of airports analyzed there is obtained through a previous clustering step,
whose results are available through the function getFlightDelayData().
For more detailed explanations of the individual methods see Vignette “applicationDanube” and the help pages of applied functions.
Note: Due to size restrictions, the CRAN version of this package contains only a part of the full dataset.
A version of this package with the complete dataset is available on GitHub.
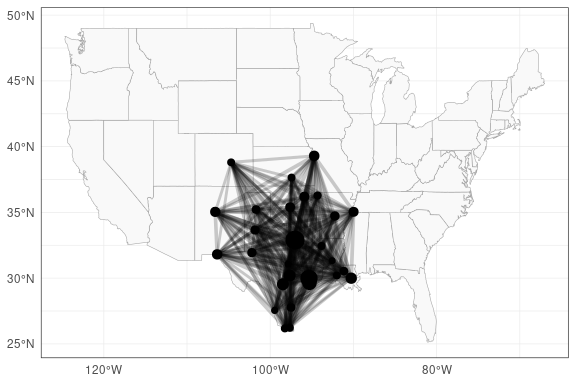
# Get IATAs from Texas cluster
IATAs <- getFlightDelayData('IATAs', 'tcCluster')
# Plot airports + connections (indicating number of flights by thickness)
plotFlights(
IATAs,
useAirportNFlights = TRUE,
useConnectionNFlights = TRUE
)
For hyperparameter tuning and model comparison purposes, we will use a train-test-split, utilizing some data to estimate the graph structure and parameter matrix, and the remaining data to compute a likelihood value.
# Check whether all dates from the train-test-split are available
# (due to size restrictions, the CRAN version of this package does not contain all dates)
allDatesAvailable <- tryCatch({
getFlightDelayData('dates', dateFilter = c('tcAll'))
TRUE
}, error = function(...) FALSE)
cat('All dates avilable:', allDatesAvailable, '\n')
#> All dates avilable: TRUE
# Create train and test data sets
if(allDatesAvailable){
# Use train-test-split and threshold p from article
matEst <- drop(getFlightDelayData('delays', 'tcCluster', 'tcTrain'))
matVal <- drop(getFlightDelayData('delays', 'tcCluster', 'tcTest'))
p <- 0.95
} else {
# Take all available dates that do not contain NAs
mat <- drop(getFlightDelayData('delays', 'tcCluster', 'all'))
rowHasNA <- apply(is.na(mat), 1, any)
mat <- mat[!rowHasNA, ]
# Split dates in half
splitInd <- floor(nrow(mat)/2)
matEst <- mat[1:splitInd,]
matVal <- mat[(splitInd+1):nrow(mat),]
# Use a lower threshold to compensate for the smaller dataset
p <- 0.8
}This function will be used later to compare fitted parameters to empirical ones.
# Compute the empirical extremal correlation matrix
emp_chi_mat <- emp_chi(matEst, p = p)
# Utility function to plot fitted parameters against true/empirical ones
plot_fitted_params <- function(G0, G1, xlab = 'Empirical', ylab = 'Fitted'){
return(
ggplot()
+ geom_point(aes(
x = G0[upper.tri(G0)],
y = G1[upper.tri(G1)]
))
+ geom_abline(slope = 1, intercept = 0)
+ xlab(xlab)
+ ylab(ylab)
)
}2 Fitting a model to the flight graph
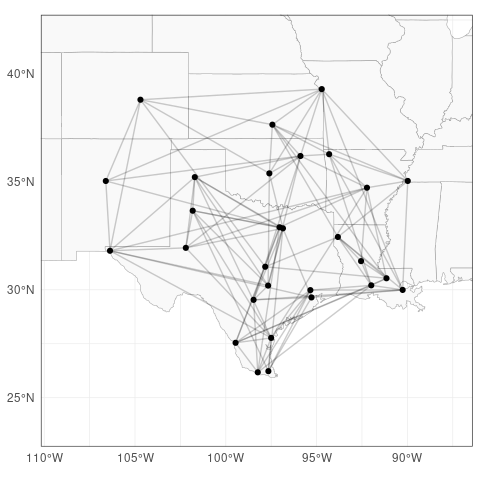
As a baseline for graphical modelling, we consider the graph with edges representing at least monthly connections between airports.
# Compute undirected flights per connection between selected airports
nYears <- dim(flights$flightCounts)[3]
flightsPerConnection <- apply(flights$flightCounts[IATAs,IATAs,], c(1, 2), sum)
flightsPerConnectionUD <- flightsPerConnection + t(flightsPerConnection)
# Make flight graph from adjacency matrix
A <- 1 * (flightsPerConnectionUD > nYears * 12)
flight_graph <- graph_from_adjacency_matrix(A, diag = FALSE, mode = "undirected")
# Plot flight graph
plotFlights(IATAs, graph = flight_graph, clipMap = 1.3, xyRatio = 1)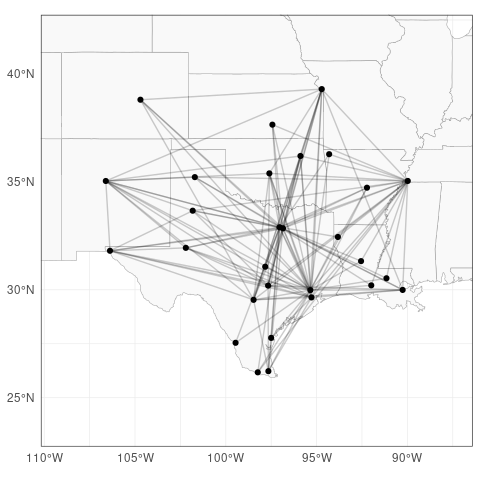
Given the flight_graph object, we fit a Hüsler–Reiss model with that graphical structure.
# Fit the model
model_fit <- fmpareto_graph_HR(
data = matEst,
graph = flight_graph,
p = p,
method = "vario"
)
#> Error in complete_Gamma(Gamma_partial, graph): Package "edmcr" is required to compute initial completion!
# Compute likelihood/ICs
flights_loglik_graph <- loglik_HR(
data = matVal,
p = p,
graph = flight_graph,
Gamma = model_fit
)
#> Error: object 'model_fit' not found
cat("Flight graph test-loglikelihood =", round(flights_loglik_graph['loglik'], 2), "\n")
#> Error: object 'flights_loglik_graph' not found
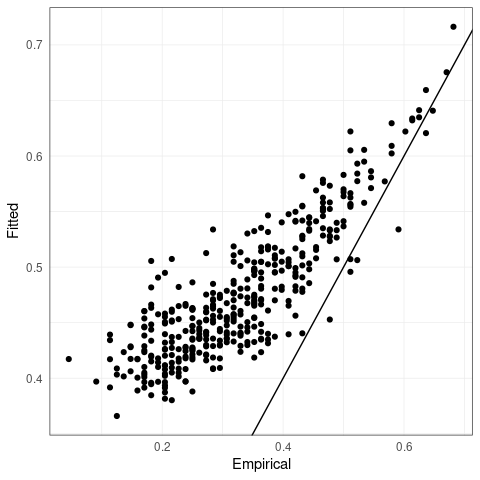
# Plot fitted parameters
plot_fitted_params(emp_chi_mat, Gamma2chi(model_fit))
#> Error in `geom_point()`:
#> ! Problem while computing aesthetics.
#> ℹ Error occurred in the 1st layer.
#> Caused by error:
#> ! object 'model_fit' not found3 Fitting a tree model
Next, we fit an extremal tree model to the flight delays using emst().
# Fit the model
flights_emst_fit <- emst(data = matEst, p = p, method = "vario")
# Compute likelihood/ICs
flights_loglik_tree <- loglik_HR(
data = matVal,
p = p,
Gamma = flights_emst_fit$Gamma,
graph = flights_emst_fit$graph
)
cat("Tree test-loglikelihood =", round(flights_loglik_tree['likelihood'], 2), "\n")
#> Tree test-loglikelihood = NA
# Plot fitted graph, parameters
plotFlights(
IATAs,
graph = flights_emst_fit$graph,
xyRatio = 1,
clipMap = 1.3
)
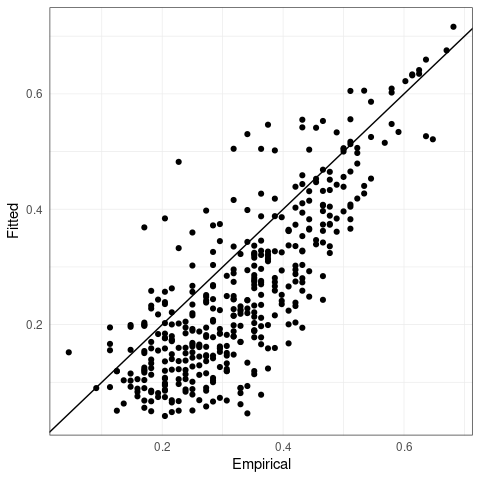
plot_fitted_params(emp_chi_mat, Gamma2chi(flights_emst_fit$Gamma))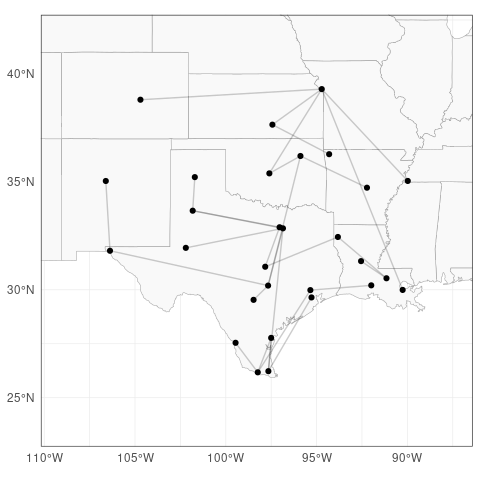
4 Fitting a general model
Lastly, we fit a general graphical model with eglearn(), using a suitable list of penalization parameters.
# Fit the model
rholist <- seq(0, 0.50, length.out = 11)
flights_eglearn_fit <- eglearn(matEst, p = p, rholist = rholist, complete_Gamma = TRUE)
# Compute likelihood/ICs
flights_loglik <- sapply(seq_along(rholist), FUN = function(j) {
loglik_HR(
data = matVal,
p = p,
Gamma = flights_eglearn_fit$Gamma[[j]],
graph = flights_eglearn_fit$graph[[j]]
)
})The “best” penalization parameter can be chosen e.g. such that the test-likelihood is maximized
ggplot(
mapping = aes(x = rholist, y = flights_loglik['loglik', ])) +
geom_line() +
geom_point(shape = 21, size = 3, stroke = 1, fill = "white") +
geom_hline(aes(yintercept = flights_loglik_graph['loglik']), lty = "dashed") +
geom_hline(aes(yintercept = flights_loglik_tree['loglik']), lty = "dotted") +
xlab("rho") +
ylab("Log-likelihood") +
scale_x_continuous(
breaks = rholist,
labels = round(rholist, 3),
sec.axis = sec_axis(
trans = ~., breaks = rholist,
labels = sapply(
flights_eglearn_fit$graph,
igraph::gsize
),
name = "Number of edges"
)
)
#> Warning: The `trans` argument of `sec_axis()` is deprecated as of ggplot2 3.5.0.
#> ℹ Please use the `transform` argument instead.
#> This warning is displayed once every 8 hours.
#> Call `lifecycle::last_lifecycle_warnings()` to see where this warning was
#> generated.
#> Error in `geom_hline()`:
#> ! Problem while computing aesthetics.
#> ℹ Error occurred in the 3rd layer.
#> Caused by error:
#> ! object 'flights_loglik_graph' not found
best_index <- which.max(flights_loglik['loglik',])
cat('Best rho =', rholist[best_index], '\n')
#> Best rho = 0.15
cat('Corresponding test-loglikelihood =', flights_loglik['loglik', best_index])
#> Corresponding test-loglikelihood = 1123.507We plot the estimated graph and parameters of the best fitted model.
best_graph <- flights_eglearn_fit$graph[[best_index]]
best_Gamma <- flights_eglearn_fit$Gamma[[best_index]]
plotFlights(IATAs, graph = best_graph, clipMap = 1.3, xyRatio = 1)
plot_fitted_params(emp_chi_mat, Gamma2chi(best_Gamma))